What is IP Spoofing ?
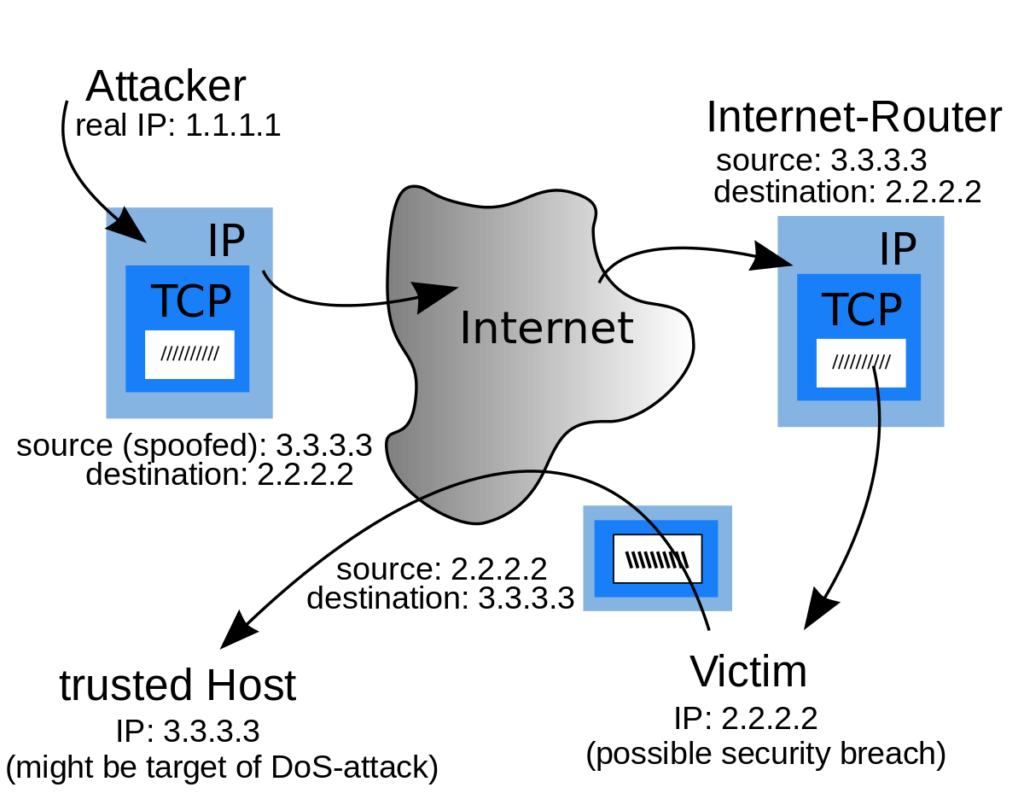
In computer networking, IP address spoofing or IP spoofing means creating packets with a false source IP address, to impersonate another computing system.
The basic protocol for sending data over the Internet is the Internet Protocol (IP). The protocol specifies that each IP packet must have a header which contains many things along with the IP address of the sender of the packet. The source IP is always the address that the packet was sent from, but the sender’s address in the header can be changed, so it appears from another source to the recipient.
IP Spoofing is used to authenticate into systems which only allow a specified IP address.
For example , in corporate networks it is common for internal systems to trust each other, so that the users can login without the credentials. By spoofing a trusted machine IP address , an attacker on the same network can access the target machine without any authentication.
IP address spoofing is mostly used in denial-of-service attacks, where the idea is to flood the target with extremely high volume of traffic, and the attacker does not care about receiving responses to the attack packets.
Services vulnerable to IP spoofing :
- RPC (Remote procedure call services)
- Any service that uses IP address authentication
- The X Window System
- The R services suite (rlogin, rsh, etc.)
IP Spoofing occurs at Layer 3, the network layer
IP Spoofing does not have a easy solution, since it’s inherent to TCP/IP suite design. Understanding how and why spoofing attacks are used, combined with a few simple prevention methods, can help protect your network.